Lichen planus blaschko-linear
Hasna Kerrouch , Meryem Khalidi, Jawad El Azhary, Rachid Frikh, Naoufal Hjira
, Meryem Khalidi, Jawad El Azhary, Rachid Frikh, Naoufal Hjira
Dermatology Venerology Department, Military Hospital Instruction Mohammed V, University Mohammed V, Rabat, Morocco
Citation tools:
Copyright information
© Our Dermatology Online 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by Our Dermatology Online.
The lines of Blaschko represent the developmental growth pattern during epidermal cell migration. They are a pattern followed by many skin disorders. Multiple clinical variants of lichen planus have been reported, but lichen planus following the Blaschko lines is extremely rare.
We present a rare case of linear lichen planus, which follows lines of blaschko.
A 43-year-old woman presented with an itching rash of 4 months duration. She had no personnel medication history and no family history of similar skin lesions.
Examination revealed linear unilateral poorly delineated purple papular and violaceus plaques along Blaschko’s lines on the lower right limb (Fig. 1). No other manifestations were noted.
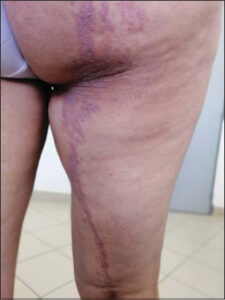 |
Figure 1: A linear unilateral poorly delineated purple papular and brownish plaques along Blaschko’s lines on the lower right limb. |
Different diagnoses were considered such as drug reaction, linear Lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP), linear lichen planus (LP), and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Routine laboratory findings did not show any abnormalities. Serological tests for hepatitis B and C virus infection were negative. A skin biopsy showed hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, an accentuated granular layer and a band-like lymphocytic infiltrate along the dermal-epidermal junction.
Unilateral Blaschko-linear LP was diagnosed.
Linear LP is a rare LP characterized by lichenoid, pruritic, violaceous papules with a smooth surface, arranging in a linear pattern [1]. Linear LP is frequently observed in childhood and the adolescent period.
The differential diagnosis of the linear variant of LP includes lichen striatus, linear psoriasis, inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus, drug reaction and linear Darier disease [2].
The diagnosis is based on clinical manifestations and histopathological findings [3].
In conclusing, Blaschkoid LP is usually benign and selflimiting. Dermatologists must be aware of this condition, so the diagnosis can be made at an early stage, improving the patient’s quality of life.
Consent
The examination of the patient was conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms, in which the patients gave their consent for images and other clinical information to be included in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due effort will be made to conceal their identity, but that anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
REFERENCES
1. Wagner G, Rose C, Sachse MM. Clinical variants of lichen planus. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2013;11:309-19.
2. Breathnach SM, Black MM. Lichen planus and lichenoid disorders. In:Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, Griffiths C, editors. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. Vol. 3, 8th edn. Oxford:Wiley-Blackwell;2010. P.42.1.
3. Munoz MA, Perez-Bernal AM, Camacho FM. Lichenoid drug reaction eruption following the Blaschko lines. Dermatology. 1996;193:66-7.
Notes
Request permissions
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the e-mail (brzezoo77@yahoo.com) to contact with publisher.
| Related Articles | Search Authors in |
|
 http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2127-3863 http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2127-3863 |




Comments are closed.