Mucocele on the tongue misdiagnosed as condyloma acuminatum
Ngo Binh Trinh 1, Nguyen Anh Thu Luu2, Giang Huong Tran3
1, Nguyen Anh Thu Luu2, Giang Huong Tran3
1Department of Dermatology, Nguyen Tat Thanh University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2Department of Pathology, Ho Chi Minh City Hospital of Dermato-Venereology, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 3Department of Pathology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy at Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Citation tools:
Copyright information
© Our Dermatology Online 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by Our Dermatology Online.
Sir,
Mucocele is caused by the accumulation of mucous secretion commonly seen on the lower lip [1]. Herein, we report a case of mucocele on the anterior ventral surface of the tongue.
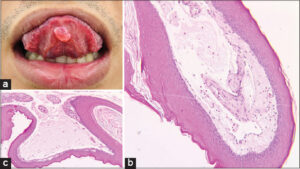
A 26-year-old male presented with a painless nodule on the tongue evolving for three months. He was clinically diagnosed with condyloma acuminatum for one month before admitting to our hospital. A physical examination revealed a painless, smooth, soft nodule, around 1 cm in diameter, on the anterior ventral surface of the tongue (Fig. 1a). Other abnormalities and lymphadenopathy were not detected. He reported no history of trauma or oral sex. Histological findings revealed a cyst-like cavity containing extravasated mucin without epithelial cyst lining (Fig. 1b). Mucin appeared diffusely in the connective tissue with proliferating capillaries and inflammatory cells (Fig. 1c). Based on the clinical and histological findings, the diagnosis of mucocele extravasation cyst was established. The entire removal was performed when doing the biopsy and no signs of recurrence were observed.
Mucocele of the tongue may be classified as a mucus extravasation cyst and a mucus retention cyst. Five cases of mucus extravasation cysts have been previously reported; however, only two cases had a similar location as ours [1,2].
The salivary glands in the tongue include the glands of Blandin–Nuhn, the glands of Weber, and the glands of von Ebner. Mucocele of the Blandin–Nuhn glands is caused by the leaking fluid of seromucous acini located on the anterior ventral surface of the tongue into the surrounding tissues [1].
The differential diagnosis of mucocele of the Blandin–Nuhn glands consists of vascular lesions, pyogenic granulomas, polyps, and squamous papilloma [3].
There is no need for treatment unless the mucocele is bothersome. Depending on the size of the mucocele, there are three possible ways of treatment, including the complete excision of the connected salivary gland tissue, the unroofing procedure, and the dissecting of the mucocele accompanied by its supporting mucous glands [2].
Mucocele on the tongue is a benign lesion, usually overlooked in our daily practice. We report this case to raise awareness and to include mucocele as a different diagnosis of excessive growths on the midline of the ventral surface of the tongue.
Consent
The examination of the patient was conducted according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms, in which the patients gave their consent for images and other clinical information to be included in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due effort will be made to conceal their identity, but that anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
REFERENCES
1. Titsinides S, Kalyvas D, Tosios K. Mucocele of the dorsal surface of the tongue:A case report. J Clin Exp Dent. 2018;10:e495.
2. Nagar SR, Fernandes G, Sinha A, et al. Mucocele of the tongue:A case report and review of literature. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol:JOMFP. 2021;25(Suppl 1):S37.
3. Sarada P, Reddy CS, Patil A, et al. Solitary nodular lesion of tongue:A rare entity. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8:256.
Notes
Request permissions
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the e-mail (brzezoo77@yahoo.com) to contact with publisher.
| Related Articles | Search Authors in |
|
 http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3829-3115 http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3829-3115 http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9480-4602 http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9480-4602 |




Comments are closed.