|
Get Citation
|
|
|
Malakar S, Pal A, Pradhan P. ‘Red starburst’ pattern: a new dermoscopic indicator in discoid lupus erythematosus. Our Dermatol Online. 2019;10(1):103-105. |
|
|
Download citation file:
|
‘Red starburst’ pattern: A new dermoscopic indicator in discoid lupus erythematosus
Subrata Malakar, Anjali Pal, Pratibha Pradhan
Rita Skin Foundation, Kolkata, India
Corresponding author: Dr. Anjali Pal, E-mail: unjelly@gmail.com
Submission: 21.03.2018; Acceptance: 04.06.2018
DOI:10.7241/ourd.20191.31
Sir,
We would like to draw attention to a peculiar dermoscopic pattern in discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) that we have noticed- we shall refer to it as the ‘red starburst’ pattern.
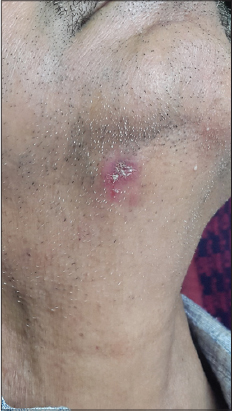
A 32 year old male presented with an asymptomatic red lesion on the right side of his neck, of 6 months duration. He had received no prior treatment for it. Clinical examination revealed an erythematous plaque with a central adherent crust, on the right side of the neck (Fig. 1). The clinical differential diagnoses were seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, DLE, and actinic keratosis.
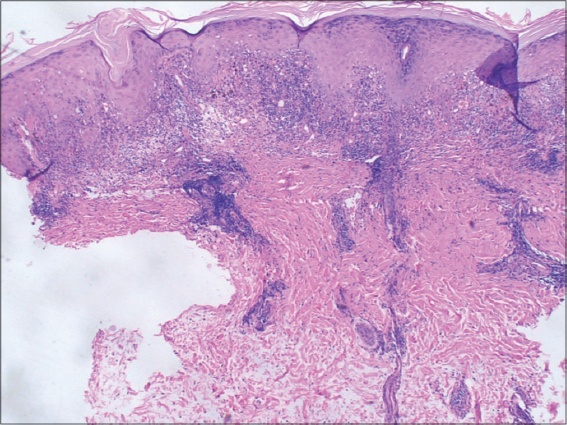
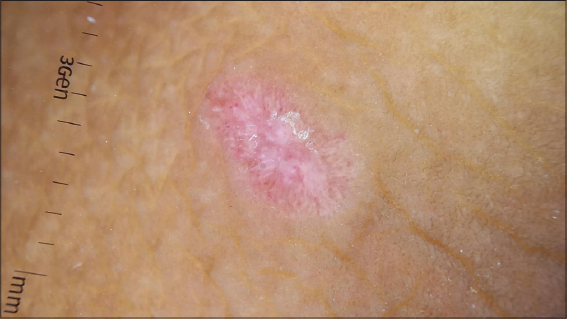
Dermoscopic examination of the lesion showed thick white scales in the centre, with blurred/out of focus radial streaks of red, along the periphery (‘red starburst’ pattern), with a surrounding whitish halo (Fig. 2). Histopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of DLE (Fig. 3).
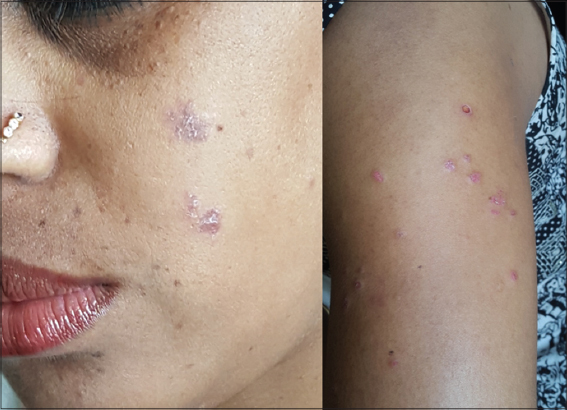
The second patient was a female aged 21 years, who presented with small erythematous scaly plaques on photo-exposed areas, of 5 months duration (Fig. 4). Dermoscopy revealed central scaling, red radial streaks, and a peripheral whitish halo. Biopsy confirmed a diagnosis of DLE.
DLE is the most common subtype of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. It occurs most frequently on the scalp, but can also involve the face, trunk and limbs [1]. The morphology of DLE varies at different stages of disease progression2.
Characteristic variables observed in dermoscopy of DLE [2] are listed in table 1.
The most common dermoscopic diagnostic criteria of these are perifollicular white halo, follicular keratotic plugs and telangiectasia [2].
The ‘starburst’ pattern was initially used to describe the dermoscopic hallmark feature of Spitz/Reed nevus. It is characterized by the presence of pigmented sharply focused streaks radially distributed at the periphery of a lesion, which correspond to confluent junctional melanocytic nests and histological radial growth [3].
A ‘white starburst’ pattern [4,5] has been described in dermoscopy of prurigo nodularis as radially arranged whitish lines on a reddish-brown background. Histopathologically, the radially arranged whitish lines correspond to papillary dermal fibrosis (the thickened collagen fibres in the papillary dermis are arranged perpendicular to the skin surface).
In the cases of DLE described above, dermoscopy revealed radially arranged red lines on an erythematous background that appear as a ‘red starburst’ pattern. Few pigment dots and globules may also be interwoven with the radial red lines.
Histopathology of long standing cases of DLE shows telangiectasia, pigmentary changes and diffuse dermal fibrosis [6]. The presence of these features are possibly reflected as a red starburst pattern dermoscopically.
Thus, we have observed that the red starburst pattern is found in long standing cases of DLE, and could be one of the specific indicators for late stage of DLE.
CONSENT
The examination of the patient was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki principles.
REFERENCES
1. Tsung-Ming T, Kuo-Chia Y. Dermoscopic features of discoid lupus erythematosus. Dermatol Sinica. 2012;30:78-80.
2. Lallas A, Apalla Z, Lefaki I, Sotiriou E, Lazaridou E, Ioannides D, et al. Dermoscopy of discoid lupus erythematosus. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:284-8.
3. Maione V, Errichetti E, Roussel SL, LebbéC. Pigmented Bowen’s disease presenting with a “starburst“pattern. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2016;6:47-9.
4. Errichetti E, Piccirillo A, Stinco G. Dermoscopy of prurigo nodularis. J Dermatol. 2015;42:632-4.
5. Ankad B S, Beergouder S L. Hypertrophic lichen planus versus prurigo nodularis:a dermoscopic perspective. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2016;6:9–15.
6. McKee P, Calonje JE, Granter S. Idiopathic connective tissue disorders. Pathology of the Skin with Clinical Correlations (Calonje JE, Brenn T, Lazar A, McKee P), 3rd ed. Amsterdam:Elsevier Mosby, 2005;775–803.
Notes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.


Comments are closed.