Methadone as an inducer of apoptotic process in cheek mucosae cells in rats
Małgorzata Stępień, Katarzyna Borowska
Department of Histology and Embryology with Experimental Cytology Unit, Medical University of Lublin, 11 Radziwiłłowska, 20–080 Lublin, Poland
Corresponding author: Prof. Katarzyna Borowska, E-mail: k_borowska@wp.pl
Submission: 06.11.2017; Acceptance: 09.11.2017
DOI: 10.7241/ourd.2017e.15
How to cite this article: Stępień M, Borowska K. Methadone as an inducer of apoptotic process in cheek mucosae cells in rats. Our Dermatol Online. 2017;8(4e):e7.
ABSTRACT
Methadone is an opioid medication which can reduce withdrawal symptoms in people addicted to heroin and other drugs. Methadone is used also as a pain reliever and as part of drug addiction detoxification program. Apoptosis is the physiological process that plays a critical role in development and tissue homeostasis. The progress of apoptosis is regulated by signal cascades. The aim of this study was to asses how methadone induces apoptotic process in cheek mucosae cells in rats. Forty albino rats wares divided into two parts and five subgroups each. The biggest histological changes of cheek mucosae was observed in the groups with methadone. There is no indication of ability to regeneration in short time after treatment.
Key words: apoptosis, caspases, methadone, rat, cheek mucosae
INTRODUCTION
Apoptosis occurs as a homeostatic mechanism to maintain cell population in tissues, and as a defense mechanism such as in immune reactions or when cells are damaged by disease or noxious agents [1]. The first time the term was used by Kerr in 1972 [2]. Apoptosis or programmed cell death mean the same. The alternative to apoptotic cell death is necrosis. The mechanisms and morphologies of apoptosis and necrosis are different. Apoptosis is a coordinated and often dependent process that involves the activation of group of cysteine proteases called caspases and a complex cascade of events that link the initiating stimuli to the final demise of the cell [3]. Apoptosis is a controlled process and energy dependent and affects individual cells. Necrosis is uncontrolled process, passive and usually affects large fields of cells. The cells are changing during apoptotic process, cells shrink, they are smaller and organelles get tightly packed. Pyknosis is the chromatin condensation and in histological examination with hematoxylin and eosin (cytoplasma is dark and nuclear chromatin is dense purple). The separation of cell fragments into apoptotic bodies is called budding. These bodies are phagocytosed by macrophages, parenchymal cells. There is no inflammatory reaction because the apoptotic body is quickly phagocytosed and their cellular constituents do not release into tissue [4]. There are two main apoptotic pathways, extrinsic via death receptor and intrinsic via mitochondrial pathway. Caspases are expressed in an inactive proenzyme and once activated can activate other procaspases and this can initiate a protease cascade. The caspases are divided into initiators – caspases 2,8,9; effectors- caspases 3,6,7; and inflammatory caspases- 1,4,5. The extrinsic signaling pathways involve transmembrane TNF. The death domain (cytoplasmic domain) plays critical role in transmitting the death signal from the cell surface to intracellular signaling pathways. Caspase 8 is activated with a death inducting signaling complex (DISC). Apoptosis can be stopped by FLIP or Toso protein and next is inhibition of caspase 8. The intrinsic signaling pathways that initiate apoptosis involve produce intracellular signals. All of these stimuli changes in the inner mitochondrial membrane, lose of potential and release proteins into cytosol. The are two groups of proteins, one consists of cytochrome c, which activates procaspase 9, forming an apoptosome. The role of apoptosis is very important to get rid the body of pathogen, dysregulation of apoptosis during wound healing can lead to pathologic tissue. It is also needed to eliminate auto aggressive immune complex. The aim of this study was to asses how methadone induces apoptotic process in cheek mucosae cells. The main objective of the experiment was how does the methadone change or not cheek mucosae during short drug test? The next question was if there is a difference in the regeneration of mucosae after 4 weeks break of taking drugs. And the last issue, if the methadone treatment impacts on activity of expression caspase 8 and caspase 9.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
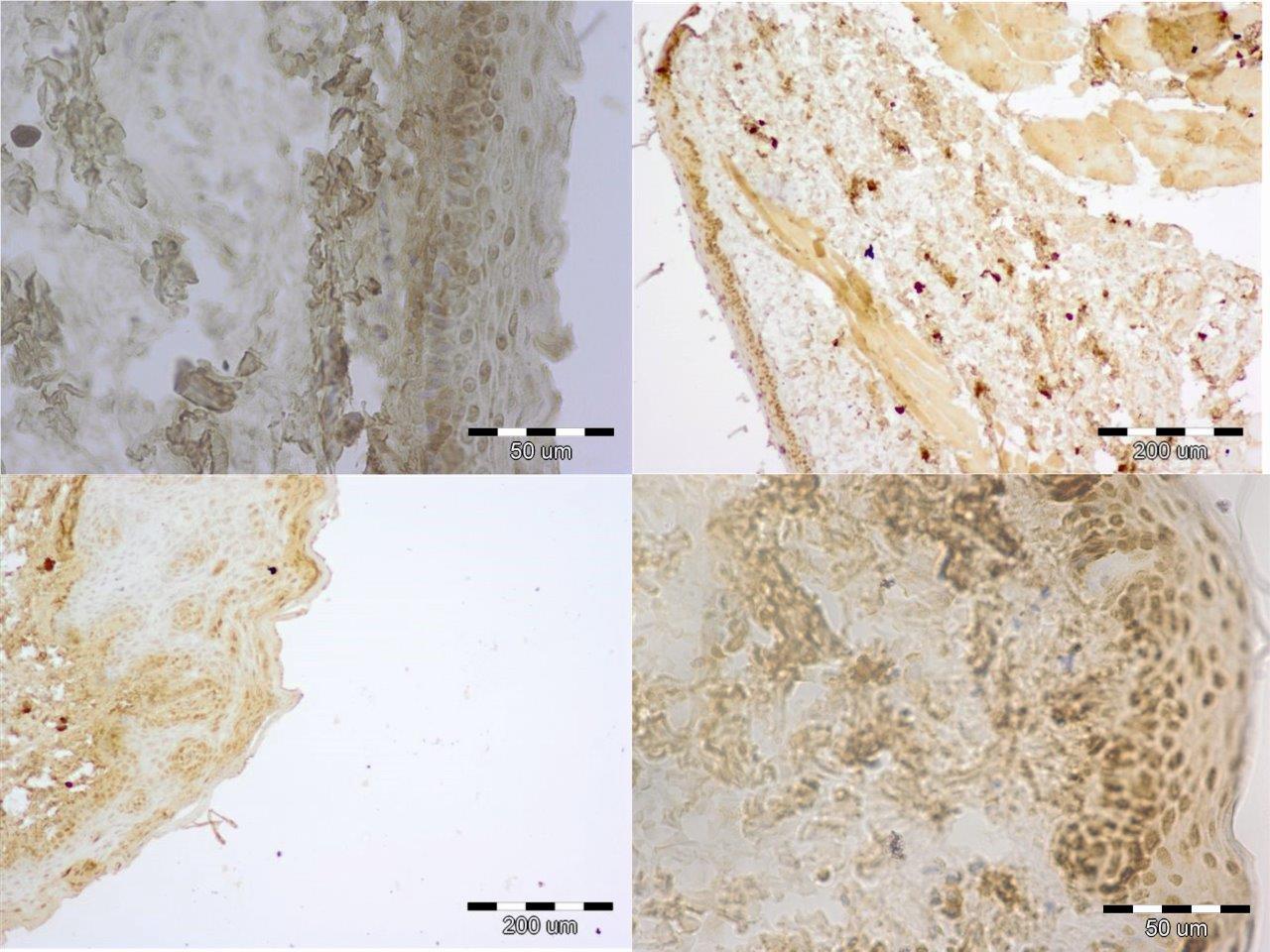
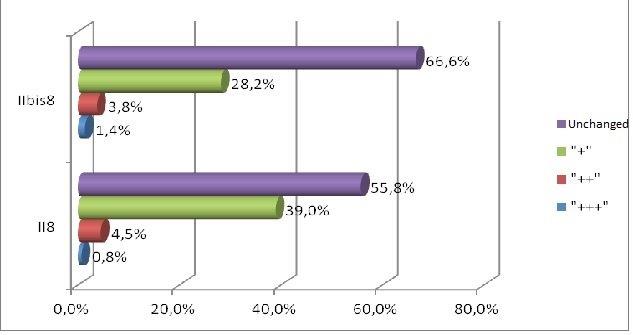
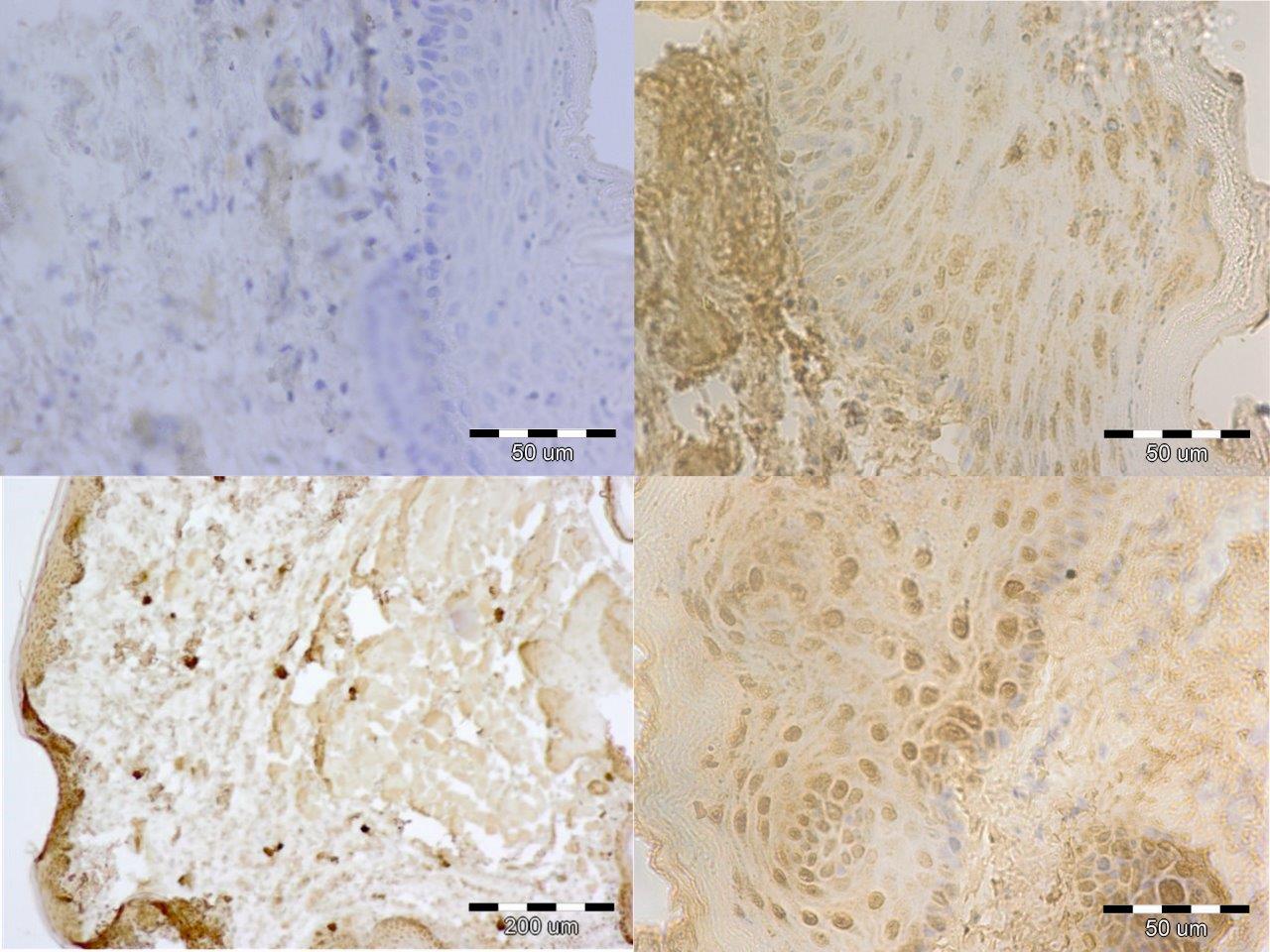
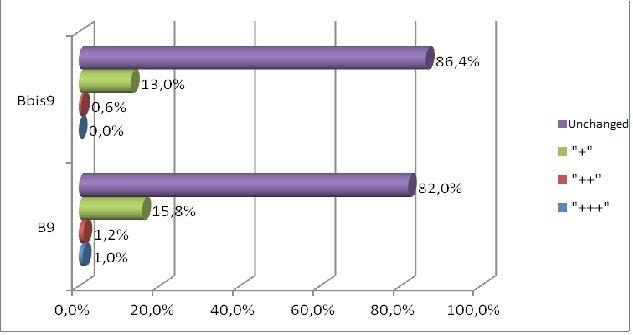
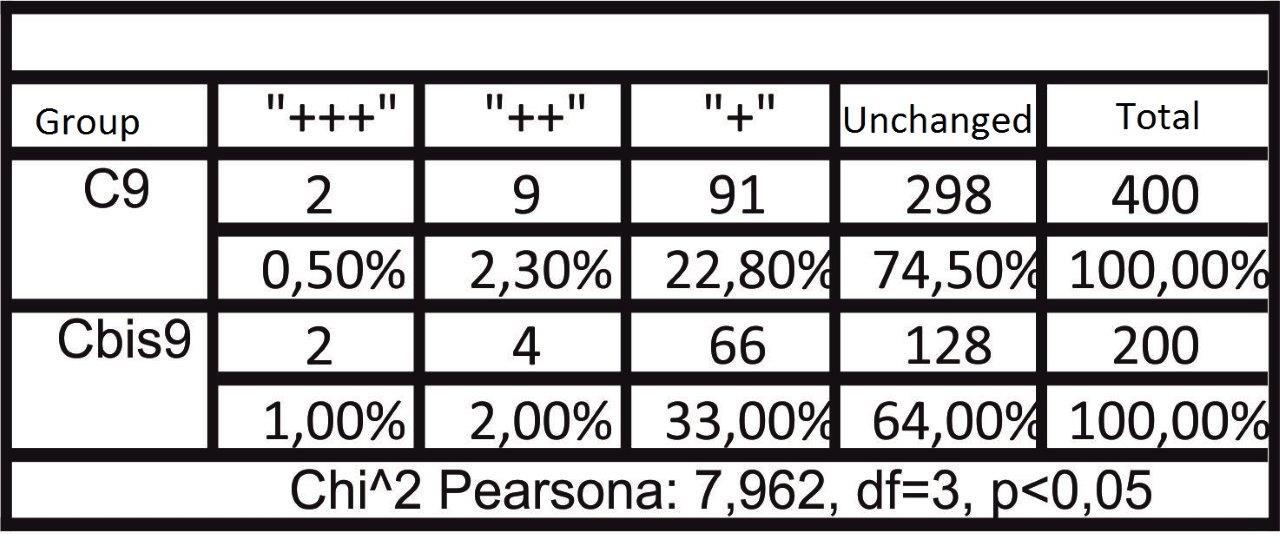
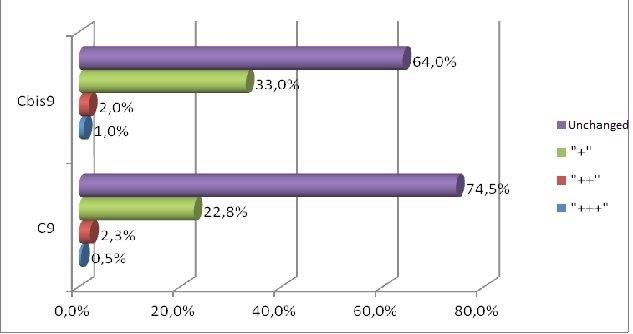
Forty male Wistar rats, weighting 200 g each (at the beginning of the experiment) were used in this research. They were kept in the same environment and fed on standard diet. The study has been approved by Medical University in Lublin 5/ 2009. The experiment was divided in two groups. The first group was sacrificed 24 hours after the last feed containing alcohol and methadone (subgroups A, B, C, II) and the second one four weeks after the last feed containing substances in question (subgroups A bis, B bis, C bis, and II bis). The animals of groups A and A bis were fed for four weeks with addition of ethanol only. In groups B and B bis both ethanol and methadone were given concomitantly (methadone starting at third week of experiment). The animals in group C and C bis were fed with addition first of ethanol and consecutively of methadone. Animals of groups II and II bis received methadone only. The control group consisted of five animals kept on typical diet without any additions. The specimens were obtained from the inside of the oral cavity – cheek, fixed, blocked and stained haematoxylin & eosin in standard procedure. The staining for immunohistochemical detection of caspase 8 and caspase 9 antigenicity was done on the same blocks. The slides were examined under the microscope at various magnifications (excluding oil immersion). Most of the digital photography documentation was taken at 200X or 400X magnfication. Histological evaluation concerns changes of number, quality and kind of cheek cells. The immunohistochemical examination of expression caspase 8 and caspase 9, was counting of apoptotic cells in the field of view. Histomorphological measurements were statistically evaluated and significance calculated by using one way ANOVA test followed by Kruskala –Wallis, Chi^2 Pearsona. All the results were expressed as mean p < 0,05, it was considered as statistically significant.
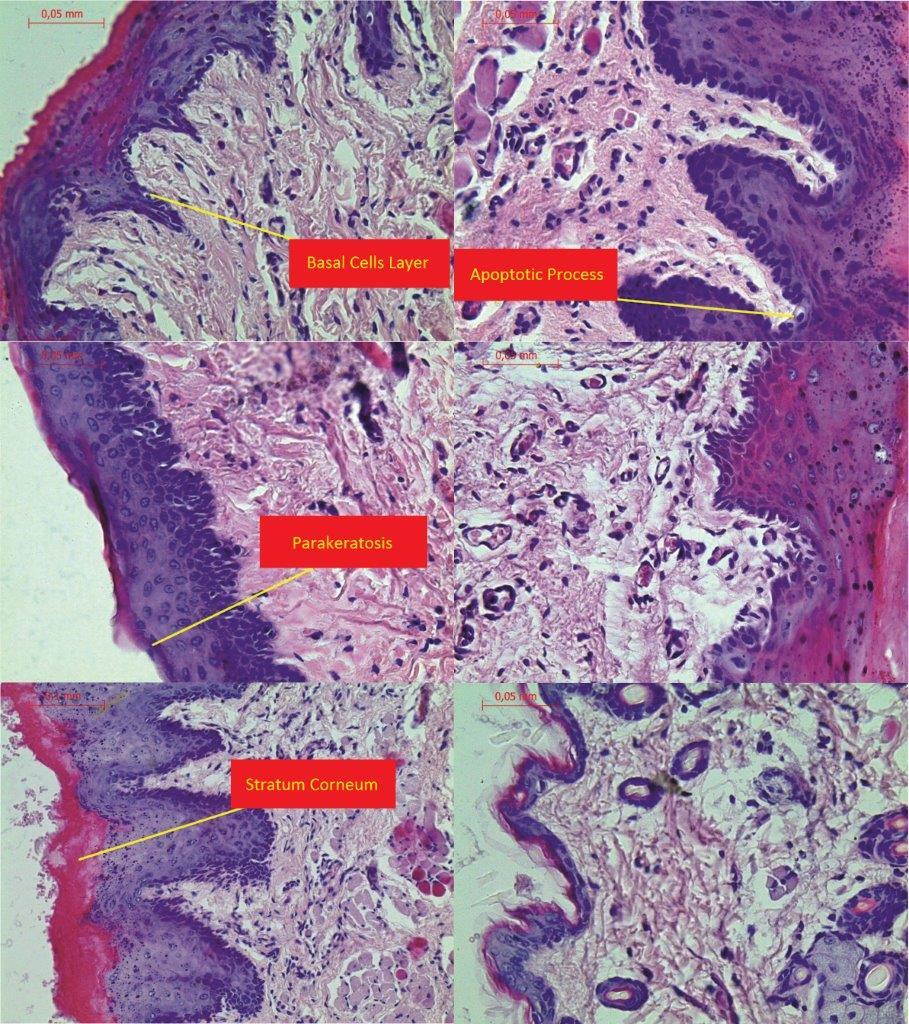
Histomorphological results
The process of apoptosis was noticed in all groups (control and treated). Histologic examination of hematoxylin and eosin stain, apoptosis involves single cells or small clusters of cells (Fig. 1). The apoptotic cells appears as round, oval mass with eosinophilic cytoplasm and dens purple nuclear chromatin fragments. Apoptotic bodies consist of cytoplasm with tightly packed organelles and parts of nuclear material. Multiple layers of viable ephitelial cells – basal layer, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum – were different images than in control group. The first was noticed the width of the layers, which were wider and ridged. The stratum basale looked like the icicles penetrating the connective tissue. The cells of the basal layer were well-defined and it may be acantotic hyperplasia. The stratum spinosum was wider, overgrown like in hypertrophy. In the cells of stratum granulosum we can see keratohialin. The connective tissue contains more cells like macrophages, parenchymal cells and the blood capillary vessels wchich were expanding. The stratum corneum was strongly marked. The results in II and II bis groups shows all the layers of the mucosae overgrowth. We noticed in group B bis (drinking alcohol and methadone together) parakeratosis and thin stratum corneum. The basal part was disturbed in group C and the apoptotic process was more intensive. Figure 1 showing H&E the treated groups.
CONCLUSION
In short term distribution of methadone was noticed influence in quality and numerous of cells of mucosae. The biggest histological changes of cheek mucosae was observed in the groups with methadone. The most marked was expression of caspase 8 in the groups with methadone. There is no indication of ability to regeneration in short time after treatment.
REFERENCES
1. Norbury CJ, Hickson ID. Cellular responses to DNA damage. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:367-01.
2. Debnath J, Baehrecke EH, Kroemer G. Does autophagy contribute cell death? Autophagy. 2005;1:66-74.
3. Mattick RP, Breen CK. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;8:CD002209
4. Joseph H, Stancliff SL. Methadone maintenance treatment; A review of historical and clinical issues. Mount Sinai J Med. 2000;67:347-64.
5. Leavitt SB, Methadone dosing & safety in the treatment of opioid addiction. Addiction Treatment Forum. 2003
6. Brondani MP. Methadone and oral health- a brief review. J Dental Hyg. 2011;85:92-8.
7. Graham CH, Meechan PE, Dental management of patients taking methadone. Dental Update. 2005;477-8, 481-2.
8. Jover R, Pansoda X, Gomez-Lechon MJ, Potentation of heroin and methadone hepatotoxity by ethanol: an in vivo study using culured human hepatocytes. Xenobiotyca. 1992;22:471-8.
9. Guo R, Ren J. Alcohol dehydrogenase accentuates ethanol-induced myocardial dysfunction and mitochondrial damage in mice: role of mitochondrial death pathway. PLoS One. 2010;18:8757.
10. Klopocka M, Budzynski J, Swiatkowski M. Wpływ 4-tygodniowej abstynencji na obraz makro-I mikroskopowej błony śluzowej górnego odcinka przewodu pokarmowego. A1 I Nark. 3003;16:87-99.
Notes
Source of Support: Nil,
Conflict of Interest: None declared.


Comments are closed.